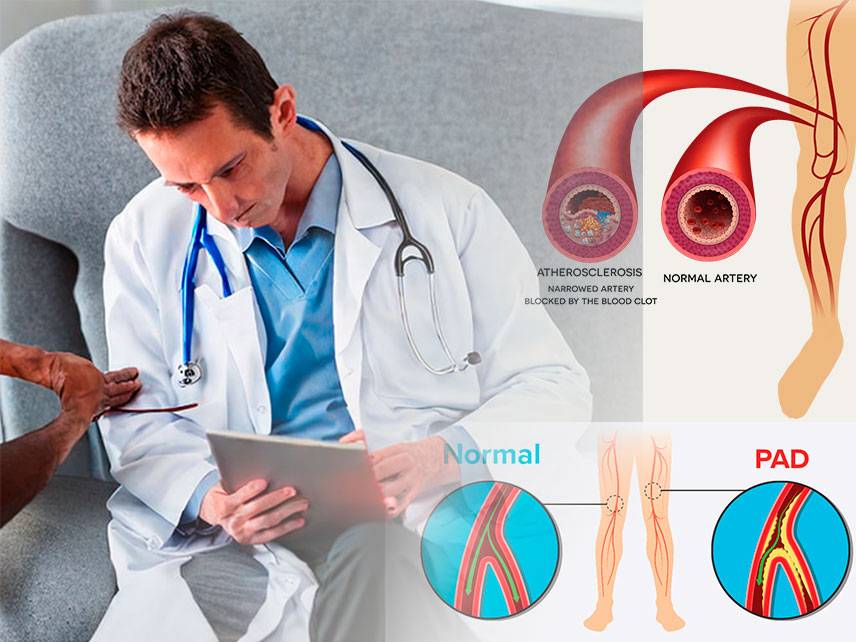
Peripheral artery disease (PAD): symptoms, diagnosis, treatment.
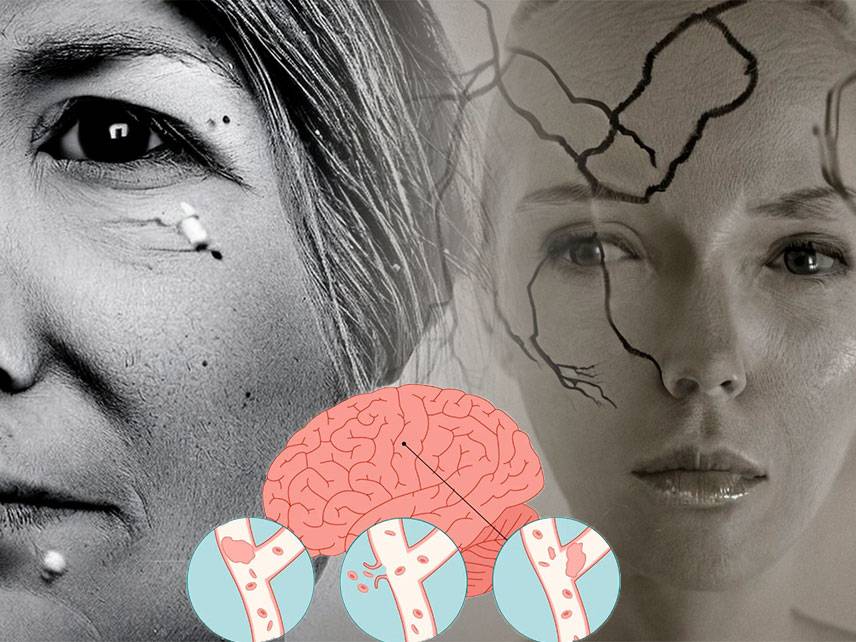
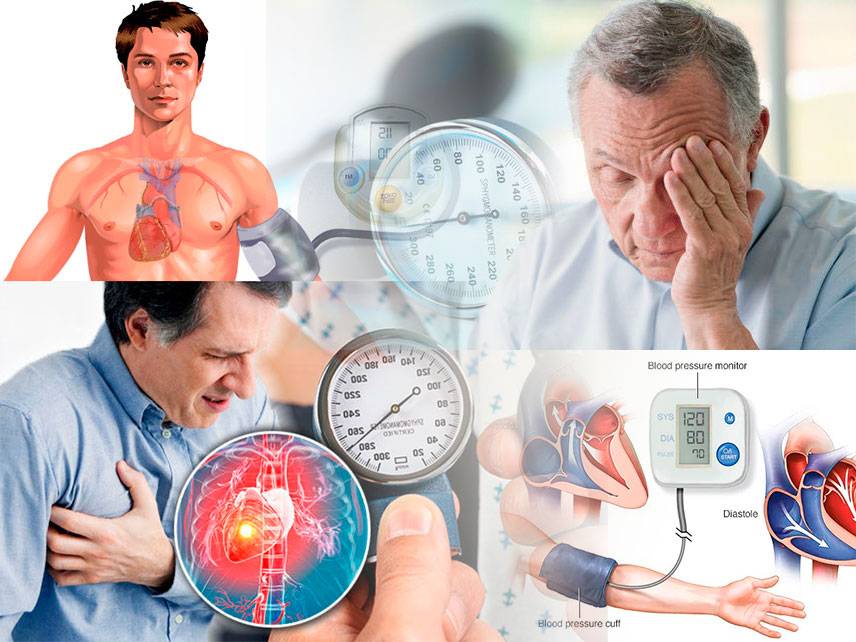
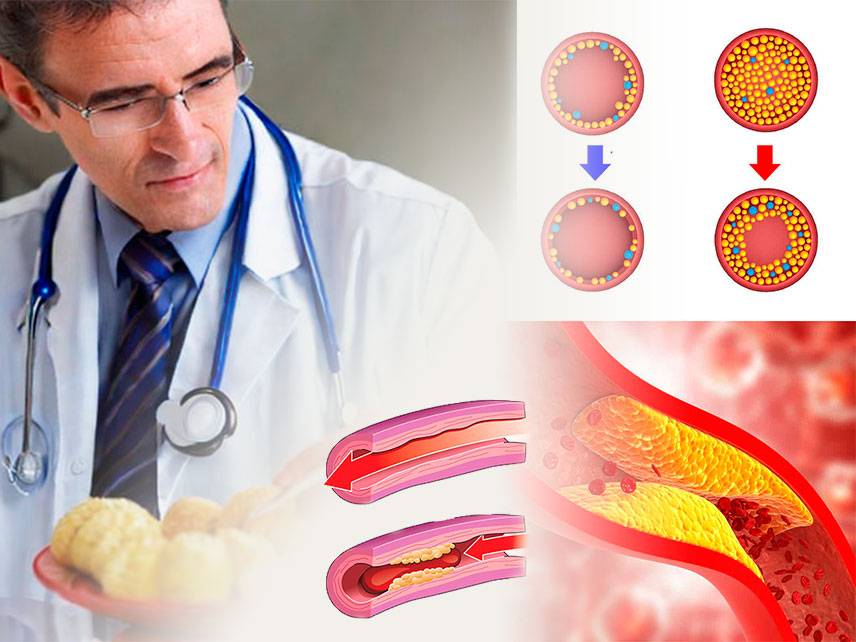
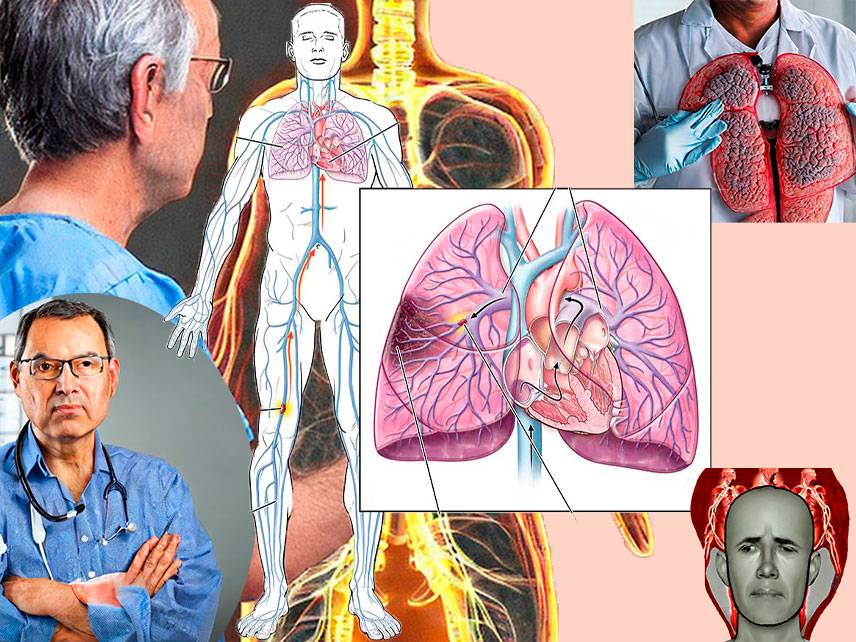
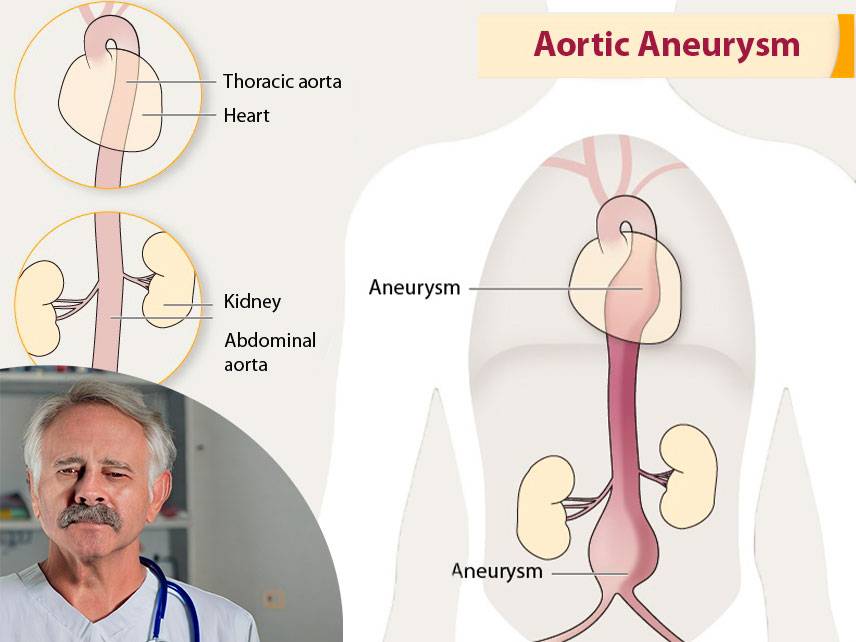
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a common circulatory problem in which plaque builds up in the arteries of the extremities, most commonly in the legs. This buildup of plaque reduces blood flow to the legs, leading to symptoms such as leg pain, numbness, and fatigue. PAD is often associated with other conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
The most common symptom of PAD is intermittent claudication, which is cramping pain in the legs that occurs when walking or exercising and is relieved by rest. Other symptoms may include leg numbness, coldness, sores that do not heal, color changes in the feet, and slow growth of toenails.
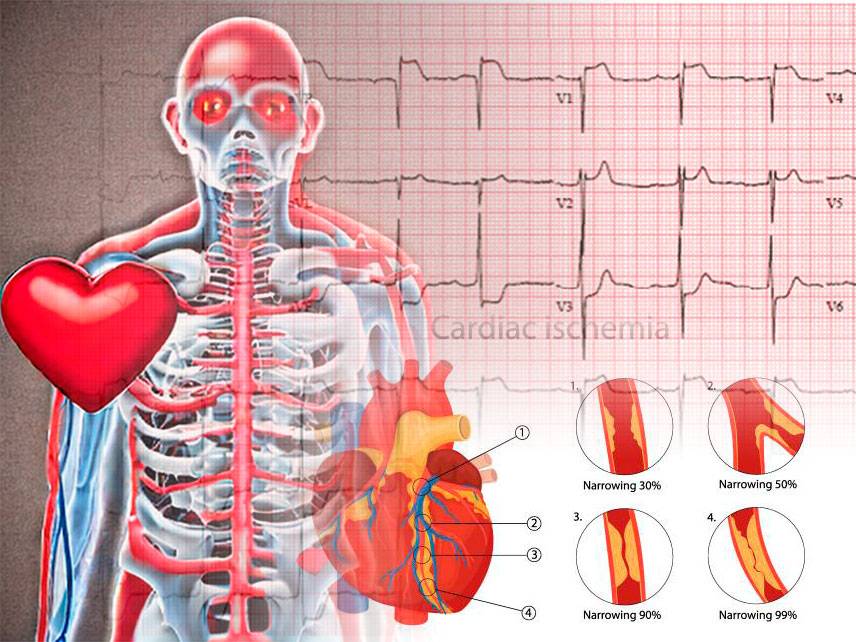
Diagnosis of PAD is done through physical exam, medical history, and imaging tests such as ultrasounds and angiograms. It is important to diagnose PAD early as it can increase your risk for heart attack or stroke.
Treatment of PAD typically involves lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, controlling your cholesterol and blood pressure, and exercising regularly. Your doctor may also prescribe medications such as statins, anticoagulants, and antiplatelet drugs. In some cases, surgery or angioplasty may be recommended to open blocked arteries.