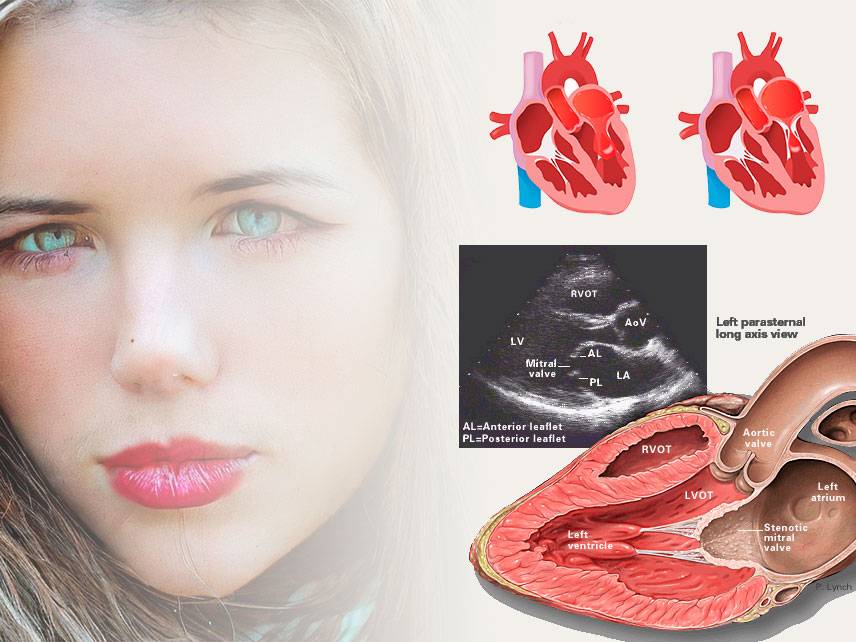
Mitral stenosis is a condition in which the mitral valve of the heart becomes narrowed, restricting blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle. This can cause a variety of symptoms, including shortness of breath, palpitations, fatigue, and chest pain. It can also lead to complications such as heart failure, stroke, or arrhythmia. Treatment for mitral stenosis typically involves medications and lifestyle modifications, but in some cases, surgery may be necessary.
Signs and Symptoms
The most common symptom of mitral stenosis is shortness of breath, which usually starts out mild but can worsen over time. Other symptoms include palpitations, fatigue, chest pain, and swelling of the legs and feet. In some cases, the patient may experience dizziness, lightheadedness, fainting, and irregular heartbeats.
Causes of Mitral Stenosis
Mitral stenosis is typically caused by rheumatic fever, an inflammatory condition that affects the heart. It is also possible for mitral stenosis to be caused by infection, radiation therapy, or a congenital defect.
Risk Factors for Mitral Stenosis
The risk of developing mitral stenosis is highest in individuals who have had rheumatic fever, have a family history of the condition, or live in an area where rheumatic fever is common. Other risk factors include age, gender, race, and existing medical conditions.
Prevention
The best way to prevent mitral stenosis is to avoid contracting rheumatic fever. This can be done by ensuring proper hygiene, avoiding contact with infected individuals, and receiving timely vaccinations.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of mitral stenosis is typically made based on the patient's medical history, a physical examination, and imaging tests such as echocardiogram or cardiac catheterization. Blood tests may also be conducted to rule out other conditions.
Treatment of Mitral Stenosis
Treatment for mitral stenosis typically involves medications to improve the symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. In some cases, lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding strenuous activities and limiting salt intake, may be necessary. If the condition is severe enough, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace the mitral valve.
Coping and Support for Mitral Stenosis
Living with mitral stenosis can be difficult, but there are a variety of resources available to help. Support groups, counseling, and lifestyle modifications can all help the patient cope with the condition and live a more fulfilling life.
Complications
If left untreated, mitral stenosis can lead to a variety of complications, including heart failure, stroke, arrhythmia, and pulmonary hypertension.
Living with Mitral Stenosis
Living with mitral stenosis can be challenging, but there are a variety of strategies that can help. Following a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding strenuous activity can all help the patient manage the condition and reduce the risk of complications. Additionally, it is important for the patient to attend regular checkups with their doctor to monitor the condition and ensure prompt treatment if necessary.