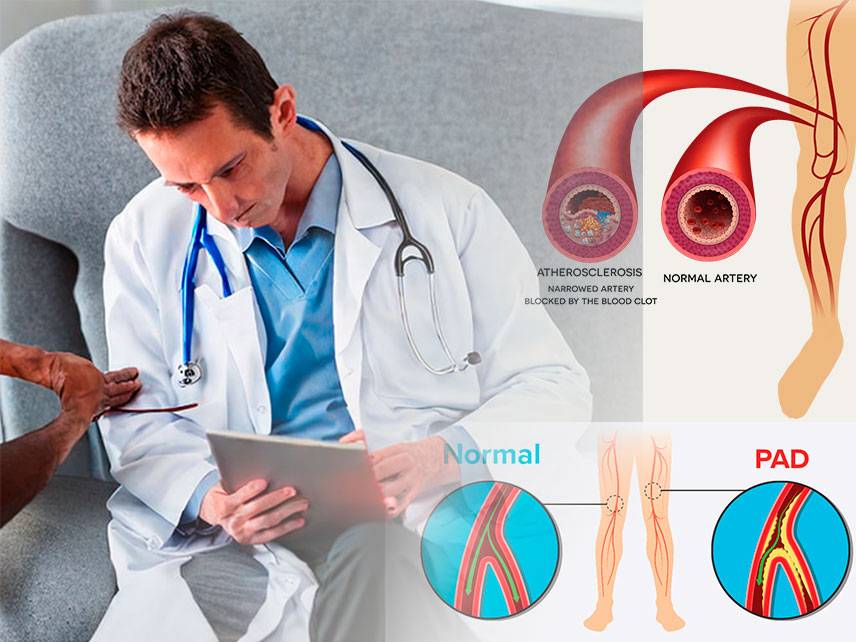
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a common circulatory problem in which narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to your limbs. PAD primarily affects the legs, but can also occur in the arms and other areas. When you develop PAD, your extremities don’t receive enough blood flow to keep up with demand. This can cause severe leg pain and make it difficult to walk.
Signs and Symptoms of PAD
The most common symptom of PAD is intermittent claudication, which is leg pain that occurs when you walk or exercise. Other symptoms may include leg numbness or weakness, coldness in your lower leg or foot, sores on your toes, feet, or legs that won’t heal, a change in the color of your legs, hair loss or slower hair growth on your feet and legs, shiny skin on your legs, or poor nail growth on your toes.
Causes of Peripheral Artery Disease
PAD is caused by a buildup of plaque in your arteries. Plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. Over time, plaque can harden and narrow your arteries. This is called atherosclerosis. When your arteries narrow, less blood can flow to your limbs, leading to PAD.
Risk Factors for PAD
The most common risk factor for PAD is age. The risk of PAD increases with age, especially after age 50. Other risk factors include smoking, diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, family history of PAD, and lack of physical activity.
Prevention of Peripheral Artery Disease
The best way to prevent PAD is to maintain a healthy lifestyle. This includes not smoking, exercising regularly, eating a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, and controlling your blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Diagnosis
Your doctor may suspect PAD based on your symptoms and medical history. To confirm a diagnosis, your doctor may order tests such as an ankle-brachial index, an ultrasound, or a CT angiogram.
Treatment of Peripheral Artery Disease
Treatment for PAD depends on the severity of the condition. In some cases, lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking and exercising regularly may be enough to improve symptoms. Your doctor may also recommend medications such as blood thinners and cholesterol-lowering drugs. In more severe cases, your doctor may recommend surgery to open blocked arteries.
What is the best treatment for peripheral artery disease?
-
Exercise
-
Medication
-
Endovascular Treatment
-
Angioplasty and Stent Placement
-
Bypass Surgery
-
Lifestyle Changes
-
Dietary Changes
-
Alternative Therapies
Coping and Support
Living with PAD can be difficult, but there are many resources available to help you cope. Support groups can provide emotional support and help you connect with other people living with PAD. You can also talk to your doctor about ways to manage your condition, such as lifestyle changes, medications, or surgery.
Complications of Peripheral Artery Disease
If left untreated, PAD can lead to serious complications such as stroke, heart attack, and gangrene. It can also increase your risk of developing an aneurysm or other vascular diseases.
Living With Peripheral Artery Disease
Living with PAD can be challenging, but there are steps you can take to improve your health and quality of life. Eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and managing your risk factors can help you manage your condition and reduce your risk of complications.
Peripheral artery disease is a common circulatory problem that can cause severe leg pain and make it difficult to walk. The most common symptom of PAD is intermittent claudication. Risk factors for PAD include age, smoking, diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, family history of PAD, and lack of physical activity. Treatment for PAD depends on the severity of the condition and may include lifestyle changes, medications, or surgery. Living with PAD can be challenging, but there are steps you can take to improve your health and quality of life.