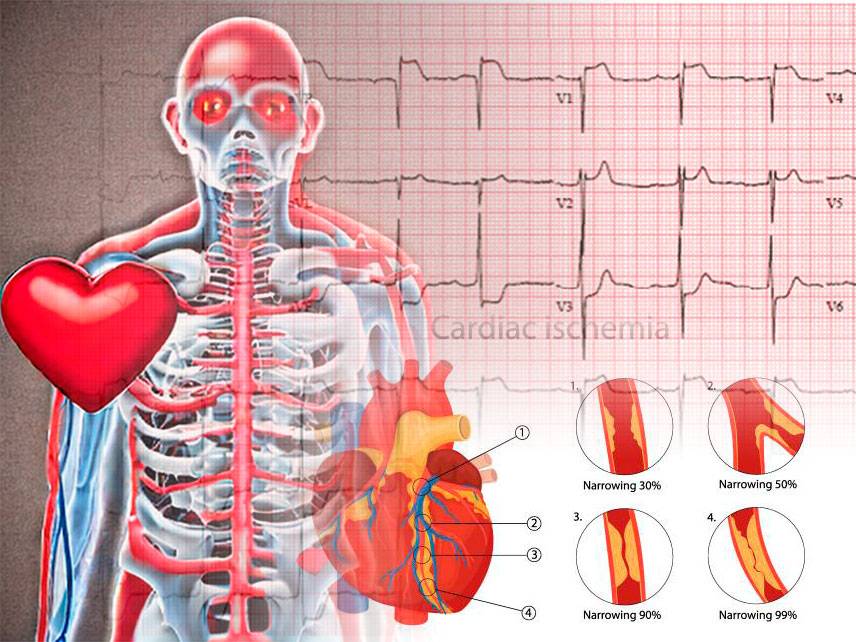
Cardiac ischemia is a condition that occurs when the heart does not receive enough oxygen-rich blood. This can cause chest pain (angina) or even a heart attack. It is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention and can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Signs and Symptoms
The most common symptom of cardiac ischemia is chest pain, usually described as a tight or squeezing sensation. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, and fatigue.
Causes of Cardiac Ischemia
Cardiac ischemia occurs when the heart does not receive enough oxygen-rich blood. This can happen due to blocked or narrowed arteries, which can be caused by a buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries (atherosclerosis).
Risk Factors
Risk factors for cardiac ischemia include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle.
Prevention
The best way to prevent cardiac ischemia is to practice a healthy lifestyle. This includes eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and controlling blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Diagnosis of Cardiac Ischemia
Cardiac ischemia is diagnosed with a physical exam and diagnostic tests such as an electrocardiogram (ECG) and stress test. Blood tests may also be ordered to check for elevated levels of certain enzymes that indicate a heart attack.
Which test is most diagnostic of cardiac ischemia?
-
Obtain a medical history from the patient to help determine the likelihood of cardiac ischemia.
-
Perform a physical examination to assess the patient’s cardiovascular system.
-
Order an electrocardiogram (ECG) to measure the electrical activity of the heart and detect any abnormal rhythms.
-
Perform a stress test to measure the heart’s response to increased physical activity.
-
Order a cardiac imaging test such as an echocardiogram or nuclear stress test to look for any blockages in the arteries.
-
If blockages are detected, order a coronary angiography to get a more detailed look at the arteries.
-
If the coronary angiography reveals any blockages, obtain a biopsy sample to determine if there is any tissue damage from the blocked arteries.
-
Finally, if the biopsy confirms tissue damage, a cardiac catheterization can be used to accurately diagnose cardiac ischemia.
Treatment of Cardiac Ischemia
Treatment of cardiac ischemia is aimed at restoring blood flow to the heart. This may include angioplasty, a procedure to open blocked arteries, or coronary artery bypass surgery. Medications such as nitrates, beta blockers, and ACE inhibitors may also be prescribed to reduce the symptoms of cardiac ischemia.
Coping and Support
Living with cardiac ischemia can be challenging and it is important to get support from family and friends. Joining a support group can also be helpful in managing the condition.
Complications
If left untreated, cardiac ischemia can lead to heart attack, heart failure, and even death.
Living with Cardiac Ischemia
Living with cardiac ischemia requires lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly. It is also important to follow your doctor’s instructions and take medications as prescribed.
Cardiac ischemia is a serious medical condition that can lead to a heart attack. It is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms and seek prompt medical attention if they occur. With proper treatment and lifestyle changes, it is possible to control and manage this condition.