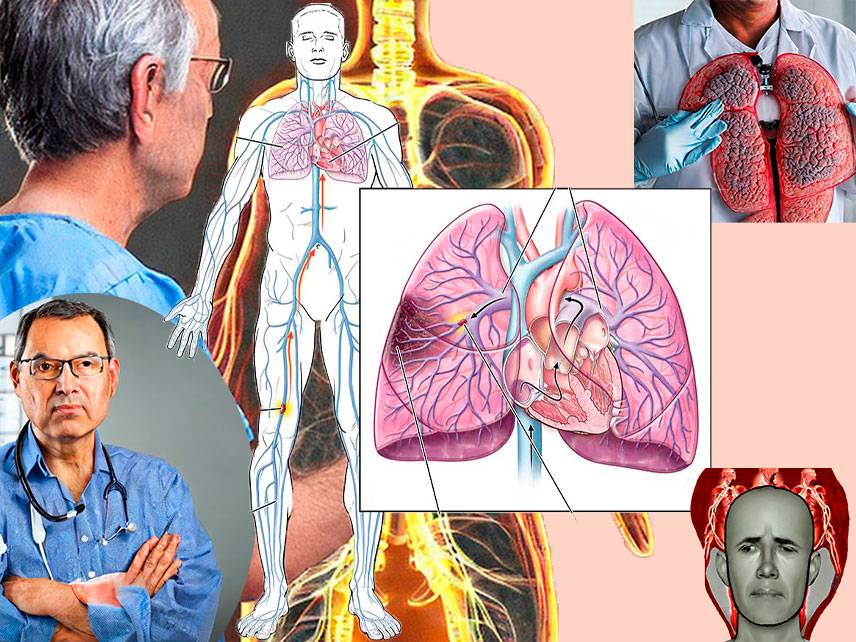
A pulmonary embolism (PE) is a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when a clot forms in the lungs and blocks an artery, preventing oxygen from reaching the lungs. The clot, which is usually a piece of a blood clot that has traveled from another part of the body, can cause serious damage to the lungs and other organs if not treated promptly. Signs and symptoms of a PE can range from mild to severe, and can even be fatal. It is important to recognize the signs and symptoms of pulmonary embolism, as well as know the risk factors, in order to seek treatment as soon as possible.
-
Signs and symptoms
-
Causes of pulmonary embolism
-
Risk factors
-
Prevention of pulmonary embolism
-
Diagnosis
-
Treatment of pulmonary embolism
-
Prognosis of pulmonary embolism
-
Coping and support
-
Complications of pulmonary embolism
-
Living with pulmonary embolism
Signs and Symptoms
The most common symptom of a pulmonary embolism is sudden shortness of breath or difficulty breathing. Other symptoms include chest pain, especially when taking a deep breath or coughing, rapid or irregular heartbeat, feeling lightheaded or dizzy, sweating, coughing up blood, and feeling anxious or panicked. If a PE is suspected, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Causes of Pulmonary Embolism
A pulmonary embolism is usually caused by a piece of a blood clot that has traveled from another part of the body and lodged in the lungs. This most commonly occurs when a clot forms in the legs or pelvis and travels to the lungs, but it can also occur when a clot forms in another organ and travels through the bloodstream.
Risk Factors
There are certain risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing a pulmonary embolism. These include being older than 60, being pregnant or recently giving birth, having a history of blood clots or having a family history of blood clots, being overweight or obese, having certain medical conditions, such as cancer or heart disease, smoking, and taking certain medications.
Prevention of Pulmonary Embolism
There are a few ways to reduce the risk of developing a pulmonary embolism. These include getting regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, not smoking, and wearing compression stockings if you are at risk for blood clots. It is also important to speak with your doctor if you are taking medications that can increase your risk of developing a PE.
Diagnosis
A pulmonary embolism is typically diagnosed with a combination of tests, including a physical exam, imaging tests, and blood tests. The physical exam may include listening to the lungs with a stethoscope to look for changes in breathing sounds, checking the pulse, and looking for signs of swelling in the legs or feet. Imaging tests, such as an X-ray or CT scan, can help to confirm a diagnosis by looking for signs of a clot or narrowing of an artery. Blood tests, such as a D-dimer test, can also help to confirm the presence of a clot.
Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism
The treatment for a pulmonary embolism will depend on the severity of the clot. Mild to moderate cases may be treated with anticoagulant medications, such as heparin or warfarin, which can help to break down the clot and prevent it from getting bigger. For more severe cases, a procedure called an embolectomy may be necessary to remove the clot from the lungs.
Prognosis of Pulmonary Embolism
The prognosis of a pulmonary embolism will vary depending on the severity of the clot and the underlying medical conditions. Most people with a PE will make a full recovery, however, it is important to seek medical attention right away if you are experiencing any signs or symptoms of a PE.
Coping and Support
Living with a pulmonary embolism can be difficult and it is important to find ways to cope with the condition. It is important to follow the doctor’s instructions and take all medications as prescribed. It can also be helpful to talk to family and friends, join a support group, or talk to a therapist or counselor.
Complications of Pulmonary Embolism
If not treated promptly, pulmonary embolism can cause serious complications. These complications include low oxygen levels, damage to the heart and lungs, and even death. It is important to seek medical attention right away if you are experiencing any signs or symptoms of a PE.
Living with Pulmonary Embolism
Living with a pulmonary embolism can be difficult, but there are ways to manage the condition and reduce the risk of complications. It is important to follow the doctor’s instructions and take all medications as prescribed. It is also important to get regular exercise, maintain a healthy weight, and avoid smoking.
A pulmonary embolism is a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when a clot forms in the lungs and blocks an artery. It is important to recognize the signs and symptoms of a PE and seek medical attention right away if you suspect you are having a PE. Treatment of a PE will depend on the severity of the clot, but most people will make a full recovery with prompt treatment. It is also important to follow the doctor’s instructions and make lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of complications.