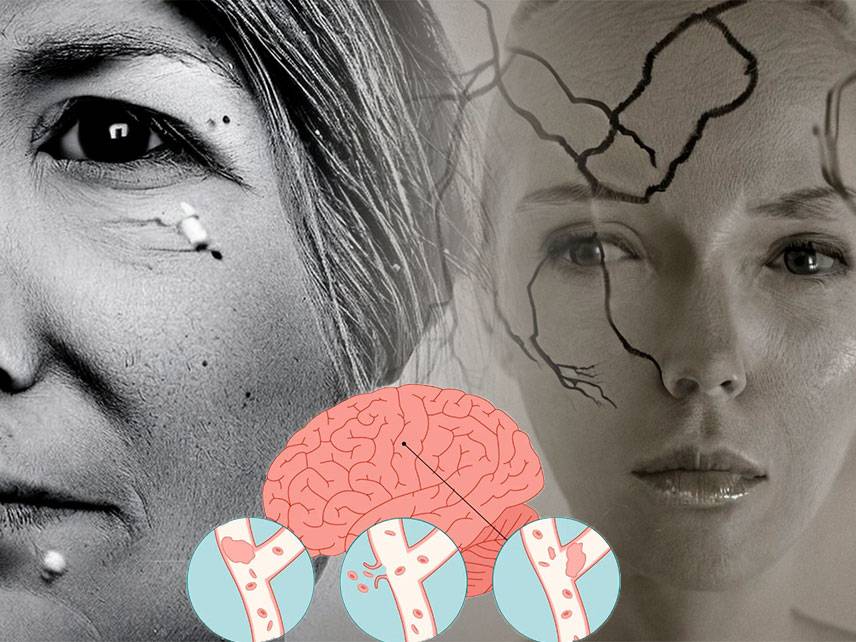
A stroke is a medical emergency that occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients. Brain cells begin to die in minutes. A stroke is a serious life-threatening medical condition that requires urgent medical attention.
-
Signs and symptoms
-
Causes of Brain stroke
-
Risk factors for Brain stroke
-
First aid for stroke
-
Prevention of Brain stroke
-
Diagnosis of Brain stroke
-
Treatment of Brain stroke
-
Coping and support
-
Complications of Brain stroke
-
Living with Brain stroke
Signs and Symptoms
The most common signs and symptoms of stroke are:
-
Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm or leg, especially on one side of the body
-
Sudden confusion, trouble speaking or understanding
-
Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes
-
Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination
-
Sudden, severe headache with no known cause
Causes of Brain Stroke
Brain stroke is caused by a disruption of the blood supply to the brain, either due to a blockage or a rupture of an artery. The blockage is usually caused by a clot (ischemic stroke) or a burst of artery (hemorrhagic stroke).
Risk Factors for Brain Stroke
Risk factors for stroke include high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, high cholesterol, and a family history of stroke. Other risk factors include atrial fibrillation, carotid artery disease, and a history of transient ischemic attack (TIA).
First aid for stroke
1. Recognize the signs and symptoms of a stroke.
These include: sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body; confusion; trouble speaking or understanding; trouble seeing in one or both eyes; trouble walking, dizziness, and loss of balance or coordination.
2. Call 911 or your local emergency medical services (EMS) immediately.
3. Provide basic life support if you are trained.
This includes checking the airway, breathing, and circulation (ABCs).
4. If the person is conscious, keep them calm and comfortable.
5. If the person is unconscious, place them in the recovery position and check their ABCs.
6. Monitor the person's vital signs, including their pulse and breathing.
7. Provide oxygen, if available.
8. If the person is having a seizure, protect them from injury and do not restrain them.
9. Keep the person warm with blankets or coats.
10. Stay with the person until EMS arrives.
Prevention of Brain Stroke
Prevention of brain stroke includes lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, not smoking, and controlling blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels.
Diagnosis of Brain Stroke
Brain stroke can be diagnosed with physical examination, imaging tests, and laboratory tests. Physical examination includes a neurological exam to examine the functioning of the nervous system. Imaging tests such as a CT scan, MRI scan, or ultrasound may be used to identify the cause of the stroke. Laboratory tests such as blood tests may be used to look for clotting or bleeding disorders.
Treatment of Brain Stroke
Treatment of brain stroke depends on the type of stroke. For ischemic stroke, treatment may include the use of clot-busting drugs such as t-PA or aspirin. For hemorrhagic stroke, treatment may include surgery to repair the damaged artery or to remove the blood clot.
Coping and Support
It is important for stroke survivors and their families to have access to support and information about stroke. Support groups, counseling, and rehabilitation can help stroke survivors and their families cope with the physical, emotional, and practical challenges of stroke.
Complications of Brain Stroke
Complications of brain stroke may include physical disability, speech and language problems, emotional and behavioral changes, and cognitive impairment.
Living with Brain Stroke
Living with brain stroke requires lifestyle changes to promote a healthy lifestyle and reduce the risk of another stroke. Eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, not smoking, controlling blood pressure, and managing other risk factors can help reduce the risk of another stroke.
Brain stroke is a serious medical condition that can lead to physical and cognitive disabilities. Treatment and prevention of stroke is important to reduce the risk of another stroke and to improve the quality of life for stroke survivors and their families.