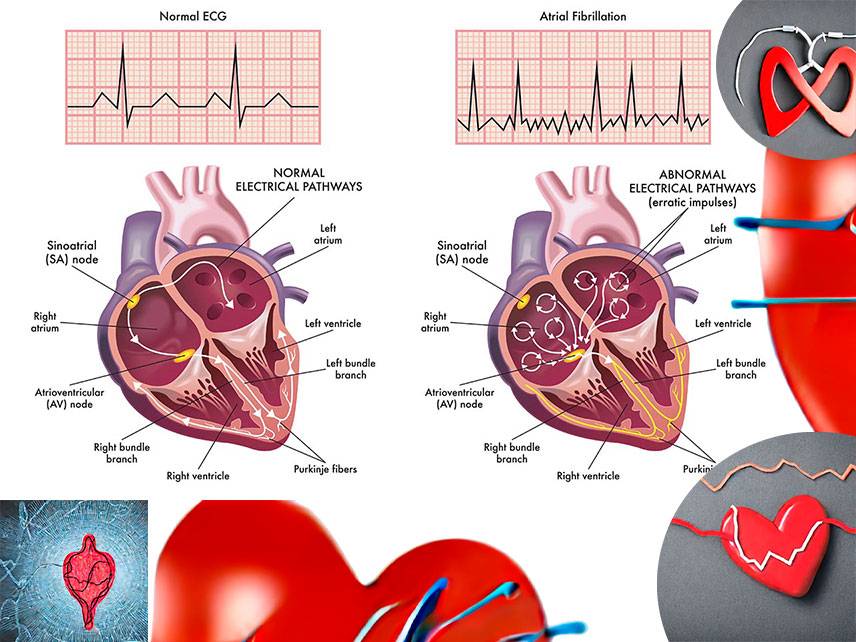
Arrhythmia and dysrhythmia are terms used to describe a disorder of the heart’s rhythm. These conditions can occur in the upper or lower chambers of the heart, and can cause a wide range of symptoms. Arrhythmia and dysrhythmia can both be serious conditions and can cause long-term complications if not treated promptly. In this article, we will discuss what arrhythmia and dysrhythmia are, the signs and symptoms, causes, risk factors, prevention, diagnosis, treatment, prognosis, coping and support, complications, and living with arrhythmia and dysrhythmia.
Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of arrhythmia and dysrhythmia can vary, depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include palpitations, chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, fainting, and fatigue.
Causes of Arrhythmia and Dysrhythmia
The most common cause of arrhythmia and dysrhythmia is a disruption in the electrical signals that control the heart rate. Other causes of arrhythmia and dysrhythmia include heart disease, high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, thyroid disease, and certain medications.
Risk Factors
Certain risk factors may increase the risk of developing arrhythmia and dysrhythmia, such as smoking, drinking alcohol, family history of heart disease, and diabetes.
Prevention of Arrhythmia and Dysrhythmia
While it is not possible to prevent all cases of arrhythmia and dysrhythmia, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk. These include quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, controlling your blood pressure, and avoiding recreational drugs.
Diagnosis of Arrhythmia and Dysrhythmia
Diagnosis of arrhythmia and dysrhythmia is typically done through a physical examination, ECG, and blood tests. If these tests are inconclusive, your doctor may order additional tests, such as a Holter monitor or an echocardiogram.
Top 7 step Diagnosis of Arrhythmia and Dysrhythmia:
-
Take the patient's medical history. This includes asking questions about any past or current heart conditions, medications, and family history of heart problems.
-
Perform a physical exam, including auscultation (listening to the heart with a stethoscope) and palpation (feeling the pulse).
-
Request an electrocardiogram (ECG) to measure the electrical activity of the heart.
-
If a dysrhythmia is suspected, order an echocardiogram (ECG) to measure the size and shape of the heart and its chambers.
-
If necessary, use an electrophysiology study (EP study) to measure the electrical activity of the heart and identify any arrhythmias.
-
Based on the results of the tests, diagnose the type of arrhythmia or dysrhythmia.
-
Develop a treatment plan to address the arrhythmia or dysrhythmia. This may include medications, lifestyle changes, or medical procedures.
Treatment
Treatment for arrhythmia and dysrhythmia depends on the type and severity of the condition. In some cases, medications may be prescribed to control the heart rate or reduce the risk of complications. Other treatments, such as surgery or catheter ablation, may be necessary in more severe cases.
Prognosis of Arrhythmia and Dysrhythmia
The prognosis of arrhythmia and dysrhythmia depends on the type and severity of the condition. Most people with arrhythmia and dysrhythmia experience no long-term complications if the condition is treated promptly.
Coping and Support
If you have been diagnosed with arrhythmia or dysrhythmia, it is important to seek support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals. Talking to others who have similar conditions may also help you to cope with your diagnosis.
Complications
If arrhythmia and dysrhythmia are not treated promptly, they can lead to serious complications, including stroke, heart failure, and even death.
Living with Arrhythmia and Dysrhythmia
If you have been diagnosed with arrhythmia or dysrhythmia, it is important to take steps to reduce your risk of complications. This includes following your doctor’s instructions, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Arrhythmia and dysrhythmia are conditions that affect the heart’s rhythm. These conditions can cause a wide range of symptoms, and can lead to serious complications if not treated promptly. If you have been diagnosed with arrhythmia or dysrhythmia, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions and make lifestyle changes to reduce your risk of complications.