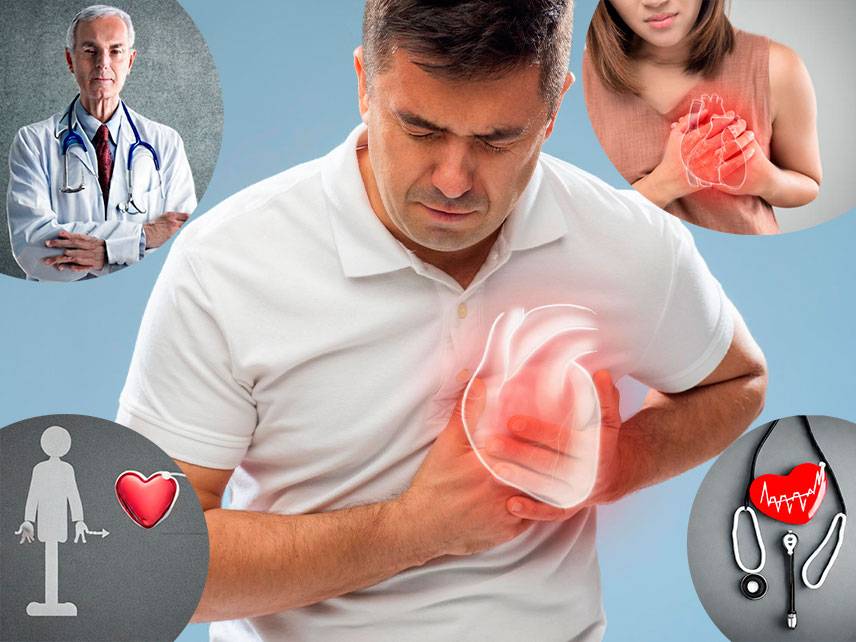
Heart failure is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. It is a progressive condition that is caused by a number of different factors and can lead to a variety of serious complications if left untreated.
Signs and Symptoms of Heart Failure
The most common signs and symptoms of heart failure include shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling (edema), and a rapid or irregular heartbeat. Other signs and symptoms may include chest pain, coughing, wheezing, increased urination, and dizziness.
Causes of Heart Failure
Heart failure can be caused by a variety of factors, including coronary artery disease, hypertension, diabetes, obesity, and abnormal heart rhythms. Other causes may include viral infections, birth defects, and certain medications.
Risk Factors for Heart Failure
Some of the risk factors associated with heart failure include age, gender, lifestyle factors (such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and inactivity), and certain medical conditions (such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol).
Prevention of Heart Failure
In most cases, heart failure can be prevented through lifestyle changes and medication. These include quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and following a heart-healthy diet.
Diagnosis of Heart Failure
In order to diagnose heart failure, your doctor will review your medical history and perform a physical exam. They may also order tests such as an electrocardiogram (ECG), chest X-ray, echocardiogram, or stress test.
Nine step diagnosis of Heart Failure:
-
Begin by obtaining a detailed patient history, including past medical history, medications, and any symptoms the patient may be experiencing.
-
Perform a physical examination, looking for signs and symptoms of heart failure, such as shortness of breath, swollen ankles and legs, rapid breathing, and a rapid heart rate.
-
Request lab tests, including a complete blood count, a chemistry panel, and a urinalysis.
-
Request an electrocardiogram (EKG) to measure the electrical activity of the heart.
-
Request an echocardiogram to measure the size, shape, and function of the heart.
-
Request an imaging test, such as a chest X-ray or computed tomography (CT) scan, to look for signs of heart failure.
-
Request a stress test to measure how well the heart is functioning during physical activity.
-
Analyze all test results to determine if a diagnosis of heart failure can be made.
-
If necessary, refer the patient to a cardiologist for further evaluation and treatment.
Treatment of Heart Failure
The goal of treatment for heart failure is to reduce symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment may include medications, lifestyle changes, and other treatments such as an implantable cardiac device or surgery.
Prognosis of Heart Failure
The prognosis of heart failure depends on the severity of the condition and the person’s overall health. In some cases, the prognosis may be poor, while in others, the condition may be managed with medications and lifestyle changes.
Coping and Support for Heart Failure
If you have been diagnosed with heart failure, it is important to find support. Support can include family and friends, support groups, and online resources.
Coplications of Heart Failure
Complications of heart failure may include heart attack, stroke, kidney failure, and fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema).
Living with Heart Failure
Living with heart failure can be difficult, but it is possible to live a full and active life with the condition. It is important to follow your doctor’s treatment plan and to make lifestyle changes to reduce your risk of complications.
Heart failure is a serious condition that can be life-threatening if left untreated. It is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms, causes, risk factors, and treatments for heart failure. With proper diagnosis and treatment, it is possible to manage heart failure and live a full and active life.