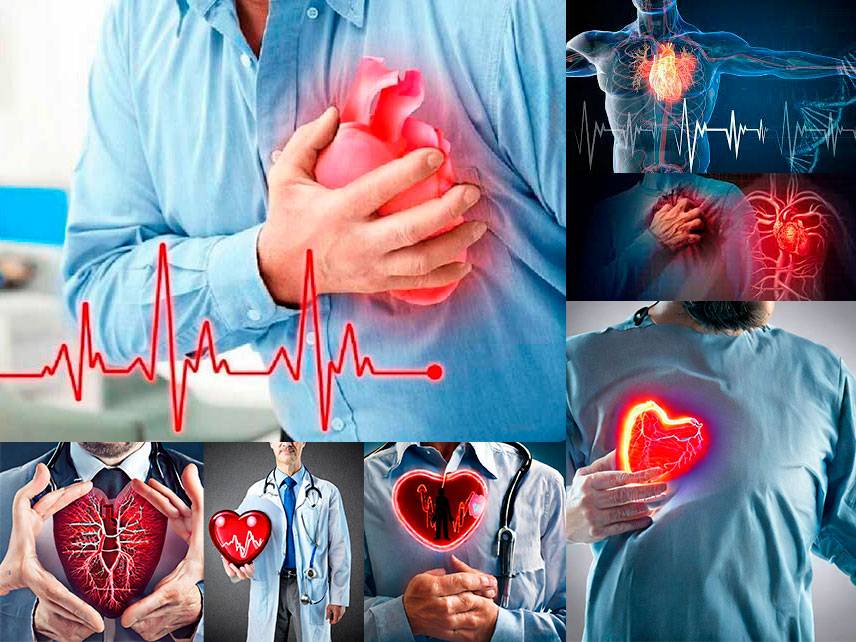
Myocardial infarction, commonly known as a heart attack, is a serious medical condition that can be fatal if not treated promptly. It occurs when a portion of the heart muscle does not receive enough oxygen-rich blood, resulting in cell death. The consequences of a heart attack can be devastating and long-lasting, so it is important to recognize the signs and symptoms and seek medical attention immediately.
Signs and Symptoms of Myocardial Infarction
The most common symptoms of a heart attack are chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, and an uncomfortable pressure, fullness, squeezing, or pain in the center of the chest that lasts more than a few minutes. Other symptoms may include nausea, sweating, dizziness, and pain or discomfort in one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
Causes of Heart Attack
The most common cause of a heart attack is a blockage in the coronary arteries, which are the blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood to the heart. This blockage is usually caused by a build-up of cholesterol-containing plaque on the walls of the arteries, a process known as atherosclerosis. Other causes of heart attack can include a spasm of a coronary artery, a sudden tear in an artery wall, or a blood clot.
Risk Factors for Myocardial Infarction
There are several risk factors for heart attack, including age, family history, smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, obesity, stress, and lack of physical activity. Knowing and controlling these risk factors can reduce the likelihood of a heart attack.
Prevention of Heart Attack
The best way to prevent a heart attack is to reduce the risk factors listed above. This includes eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, not smoking, and managing any existing conditions, such as diabetes and high blood pressure.
Diagnosis of Myocardial Infarction
If a heart attack is suspected, a doctor will usually order tests such as an electrocardiogram (ECG), blood tests, and imaging tests such as an echocardiogram. These tests can help diagnose a heart attack and determine the extent of the damage.
First aid for myocardial infarction (heart attack)
1. Call 911 or your local emergency services immediately.
2. Administer CPR if the person is unresponsive.
3. Monitor the person's airway, breathing, and circulation (ABCs).
4. Administer oxygen as necessary.
5. Monitor vital signs (blood pressure, pulse, and respiration).
6. Administer nitroglycerin, if available, and as directed by medical personnel.
7. Monitor for signs of shock or bleeding and provide support as necessary.
8. Monitor for signs of cardiac arrest and provide CPR if needed.
9. Provide emotional support as needed.
10. Keep the person comfortable until medical help arrives.
Treatment of Heart Attack
The treatment of a heart attack depends on the severity of the condition. Treatment may include lifestyle changes, medications, such as blood thinners and cholesterol-lowering drugs, and medical procedures such as angioplasty and stenting. In some cases, surgery may be necessary.
Prognosis of Myocardial Infarction
The prognosis for a heart attack depends on the extent of the damage and the patient’s overall health. In some cases, the damage can be reversed with lifestyle changes and medical treatment. In other cases, it can lead to serious complications, such as heart failure or even death.
Coping and Support for Heart Attack
Recovering from a heart attack can be a difficult and overwhelming process. It is important to have a support system in place, including family, friends, and health care professionals, to help you cope with the physical and emotional challenges of recovery.
Complications of Myocardial Infarction
Complications of a heart attack can include arrhythmia, heart failure, and stroke. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if any of these complications occur.
Living After a Heart Attack
Living after a heart attack can be challenging. It is important to follow your doctor’s instructions and make lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly. It is also important to manage any existing conditions, such as diabetes and high blood pressure, and to take all medications as prescribed.
Myocardial infarction, or heart attack, is a serious medical condition that can have life-threatening consequences. It is important to recognize the signs and symptoms, seek medical attention immediately, and take steps to reduce the risk factors. With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, it is possible to make a full recovery.